PF & IICT_Quiz1
PF
Topic#1
Variable Declaration
Variable must be declared before they are used in the program.Once declared the compiler obtain the name of variable and compiler is notify about data type of the variable being declared and help in allocation of the memory.
Syntax:
data_type variable_name;
Example:
int num;
float a;....e.t.c.
Initialization of variable
When a variable is declared,appropriate number of bytes are reserved for that variable in memory (RAM).Bytes are reserved by the garbage value if the user does not assign any value.If user perform any function without initialization of a variable then the result will be unexpected.So, before using a variable it is essential to initialize it.If the user initialize the variable then the garbage value is removed.
Initialization of a variable can be done at any where in the program or at the time of declaration before there use.
Syntax:
variable_name=constant;
or
data_type variable_name=constant;
Example:
num=12;
char a='S';
Topic#2
Cin & Cout
cin:
cin is an object of the input stream and is used to take input from input streams like files, console, etc.cin is an input statement. cin uses the insertion operator( >> ).
For formatted input operations: cin is used together with the extraction operator, which is written as >> (i.e., two "greater than" signs). This operator is then followed by the variable where the extracted data is stored. For example:
| |
cin uses the type of the variable after the >> operator to determine how it interprets the characters read from the input; if it is an integer, the format expected is a series of digits, if a string a sequence of characters, etc.cout:
cout is an object of the output stream that is used to show output. Basically, cout is an output statement. cout uses the insertion operator( << ).
For formatted output operations: cout is used together with the insertion operator, which is written as << (i.e., two "less than" signs).
| |
<< operator inserts the data that follows it into the stream that precedes it. In the examples above, it inserted the literal string Output sentence, the number 120, and the value of variable x into the standard output stream cout. Notice that the sentence in the first statement is enclosed in double quotes (") because it is a string literal, while in the last one, x is not. The double quoting is what makes the difference; when the text is enclosed between them, the text is printed literally; when they are not, the text is interpreted as the identifier of a variable, and its value is printed instead.Topic#3
Relational & Logical Operators
Go to this post which i have already share:
Topic#4
if statements
C++ if Statement:
if (testExpression)
{
// statements
}
The
if statement evaluates the test expression inside parenthesis.
If test expression is evaluated to true, statements inside the body of
if is executed.
If test expression is evaluated to false, statements inside the body of
if is skipped.How if statement works?

Flowchart of if Statement:

C++ if...else:
The
if else executes the codes inside the body of if statement if the test expression is true and skips the codes inside the body of else.
If the test expression is false, it executes the codes inside the body of
else statement and skips the codes inside the body of if.How if...else statement works?
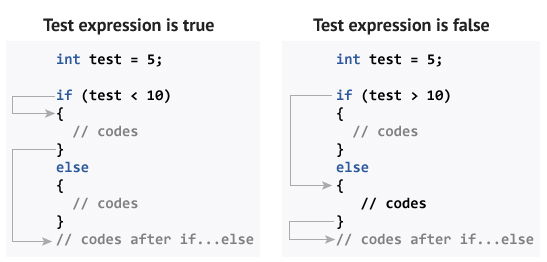
Flowchart of if...else:
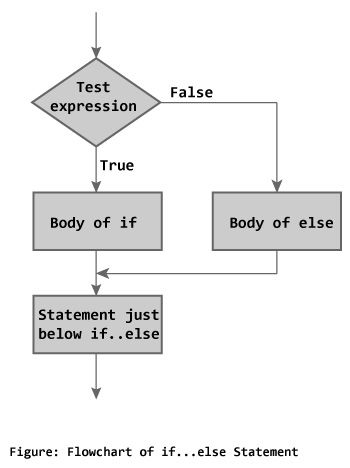
C++ Nested if...else:
The
if...else statement executes two different codes depending upon whether the test expression is true or false. Sometimes, a choice has to be made from more than 2 possibilities.
The nested
if...else statement allows you to check for multiple test expressions and execute different codes for more than two conditions.Syntax of Nested if...else:
if (testExpression1)
{
// statements to be executed if testExpression1 is true
}
else if(testExpression2)
{
// statements to be executed if testExpression1 is false and testExpression2 is true
}
else if (testExpression 3)
{
// statements to be executed if testExpression1 and testExpression2 is false and testExpression3 is true
}
.
.
else
{
// statements to be executed if all test expressions are false
}



Comments
Post a Comment